Art as an Experience
Throughout history, individuals have utilized different mediums to convey their creativity. Humans have been associated with art from ancient times dating back to cave paintings where the abstracted imagery of animals and people depicted the way of life of the community on the walls of the caves and continued through the Renaissance with the realistic portrait of Monalisa. Over time, this medium has shifted from physical means to virtual platforms. The art world has been profoundly impacted by digital technology, which has changed how we create, experience, and consume art. Especially artists who are continually adapting their methods of artistic expression. Consequently, art has become even more varied, inventive, and dynamic than in previous eras. Art has not remained just a physical two-dimensional medium but has reached the capabilities of reaching an immersive experience of hearing, smelling, and feeling the art.
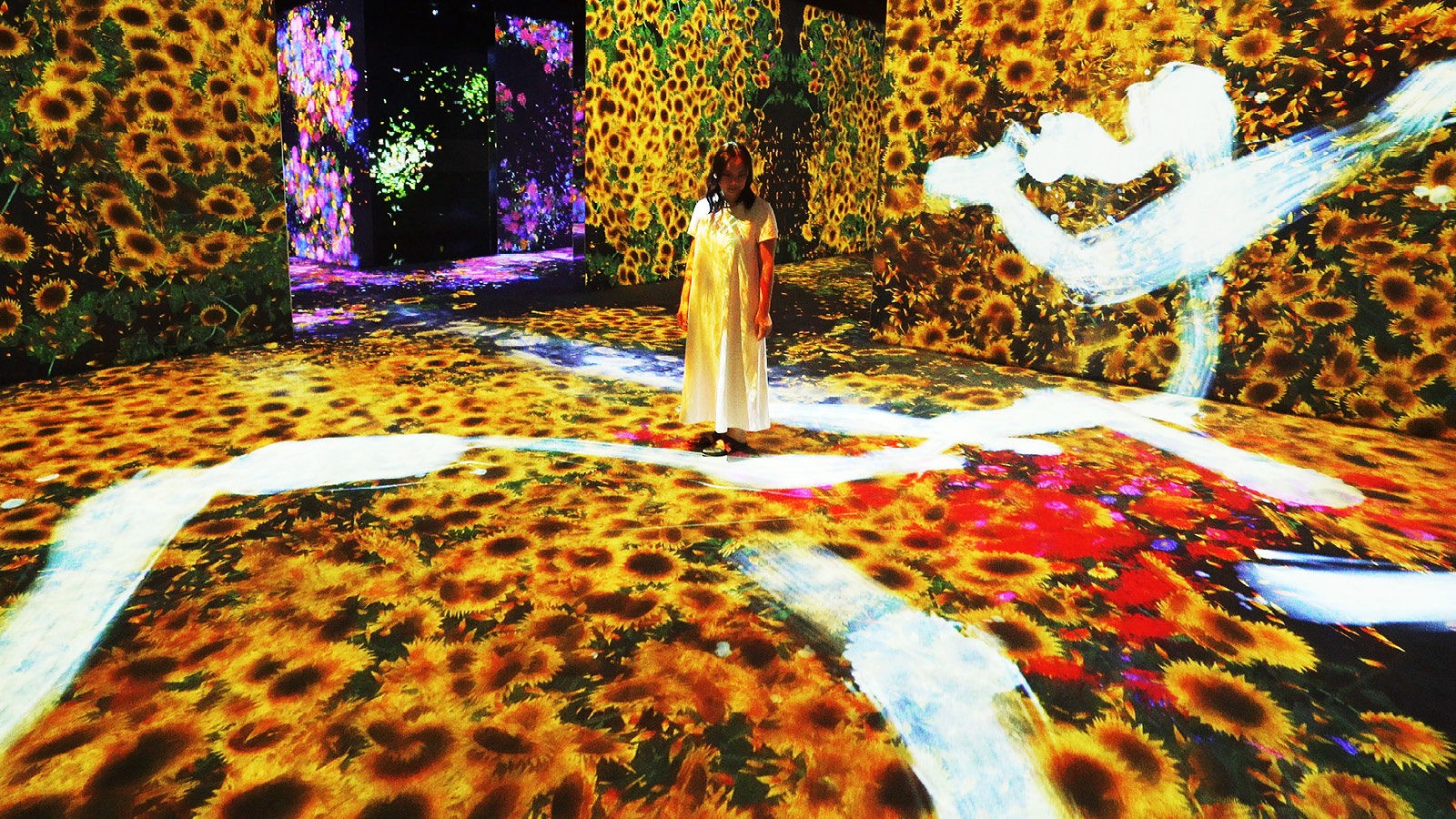
For example, in San Francisco’s Asian Art Museum, an immersive art experience illustrates a wondrous ecosystem of lush imagery drawn from East Asian art drawing strong inspiration from nature. The environment develops dynamically with enchanting music, the lingering smell of flowers along with captivating images encouraging the observer to wander, take moments of pause, and be filled with a sense of wonder and admiration.

Role of Digital Technology in Immersive Art
Given the constantly evolving technological terrain, ‘digital art’ has now encompassed a wide array of artistic ventures, evolving into an expansive and virtually boundless art movement. Ranging from Digital Painting, 3D Sculpting and Painting, Animation, and photography, etc these different mediums provide artists with countless ways to express themselves uniquely. However, the recent developments in the digital world of art creation namely AR VR, Motion Graphics, and to a whole new level of Artificial Intelligence have helped art reach a new tangent.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality (VR) uses the medium of a headset to transport individuals into alternate realms, granting artists complete control over the novel dimensional space perceived through the lens. As a result, it provides a way to detach the audience from reality by immersing them in engaging and imaginative realms.
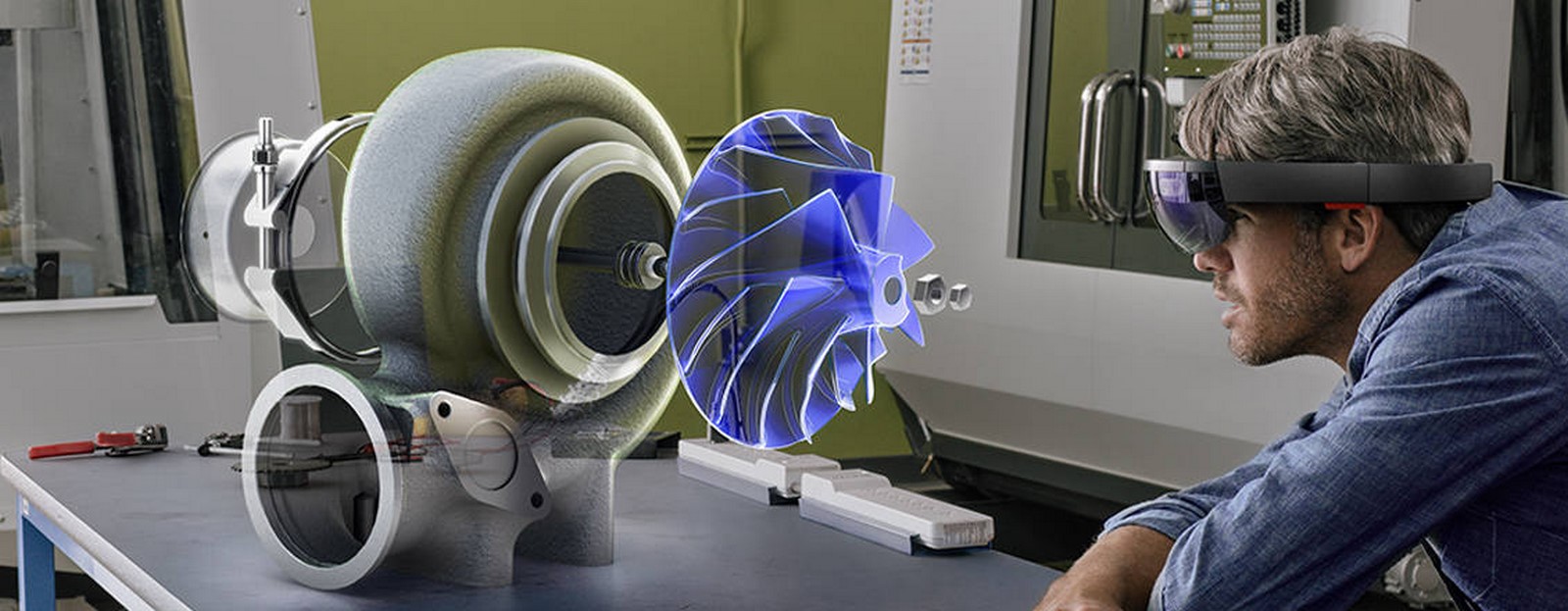
In contrast to virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) uses technology and visual advancements to improve the audience’s sense of reality rather than disconnecting them from the real world. Artists can craft incredibly immersive experiences, allowing audiences to interact with the art in a three-dimensional environment. For Example, Renowned for his fusion of classical art, technical animation, and immersive technology, the artist of the Macro-O-Matic infuses a vintage steampunk aesthetic. Through mobile devices, spectators gain a more profound insight into his artworks. By directing their phones toward an artwork, augmented reality breathes life into it with animated visuals and accompanying sound, enriching the narrative behind the piece.
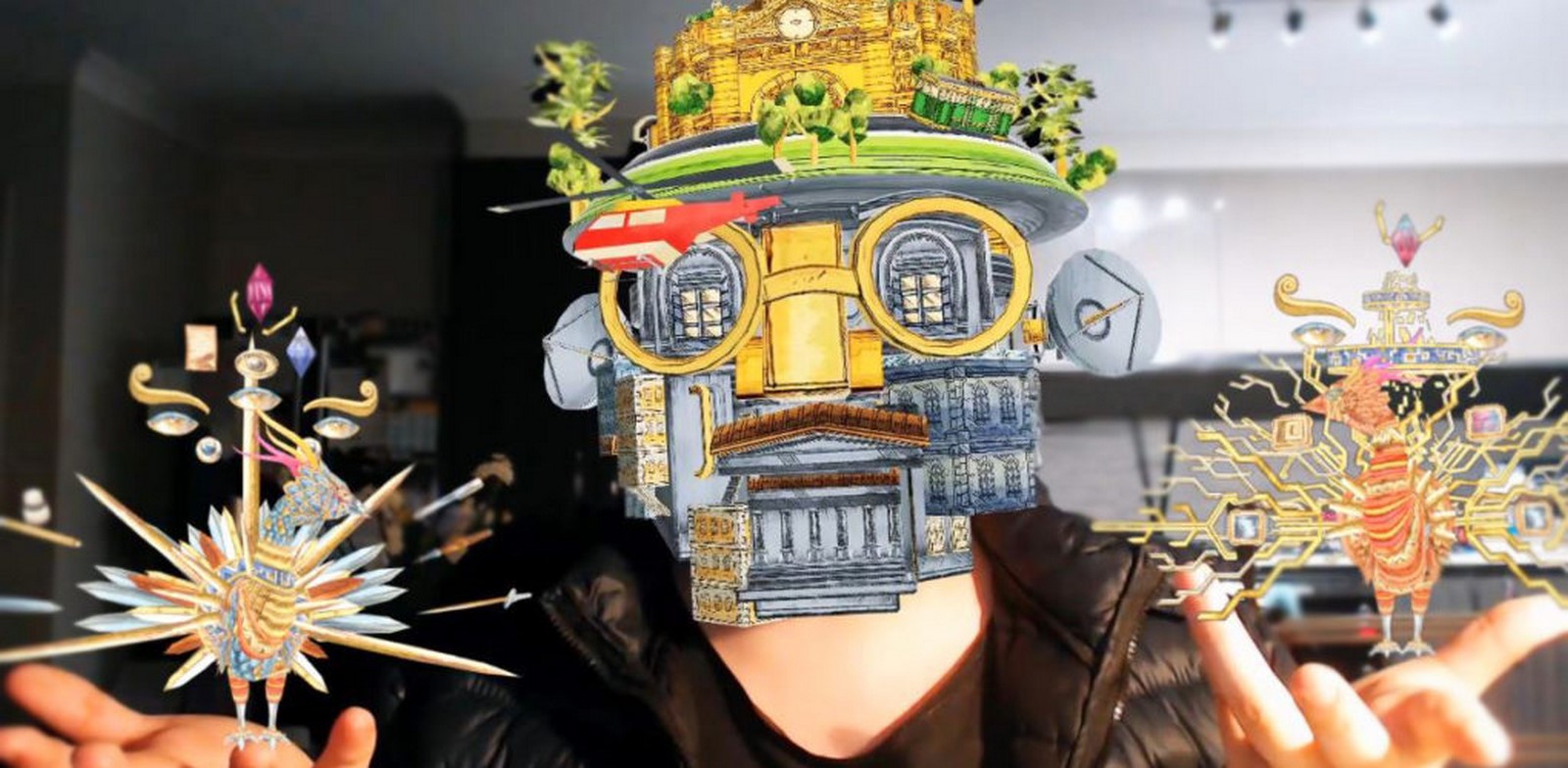

Art is creating emotions, feelings, and deep thoughts in the person who is looking; art is sharing terrifying secrets and revolutions while creating beauty. Augmented Reality can enhance all of this. These mediums represent a natural progression in the realm of artistry, and it is foreseen that artists will persist in experimenting with these forms, propelling this technology into innovative and uncharted territories of creativity. This evolution promises to unlock fresh avenues for artistic expression and audience engagement.
- Motion Graphics Animation
Skeletal-based animation gives creators the ability to work with 3D modeling and sculpting to produce finished 3D animations. Filmmakers can generate incredibly realistic and high-definition three-dimensional movie animations using tools like CGI. With advances like the facial animation technique that was first seen in “Avatar: The Way of Water,”.The technology employed was grounded in the utilization of the Facial Action Coding System (FACS), which integrated a head rig alongside a standard-definition camera to capture the expressions of the actor, whose face was adorned with computer-readable markers. Two massive tanks were built, one with a 250,000-gallon capacity for extensive action sequences using a wave generator submerged for surface interactions was placed above the tank and the other for underwater shots.
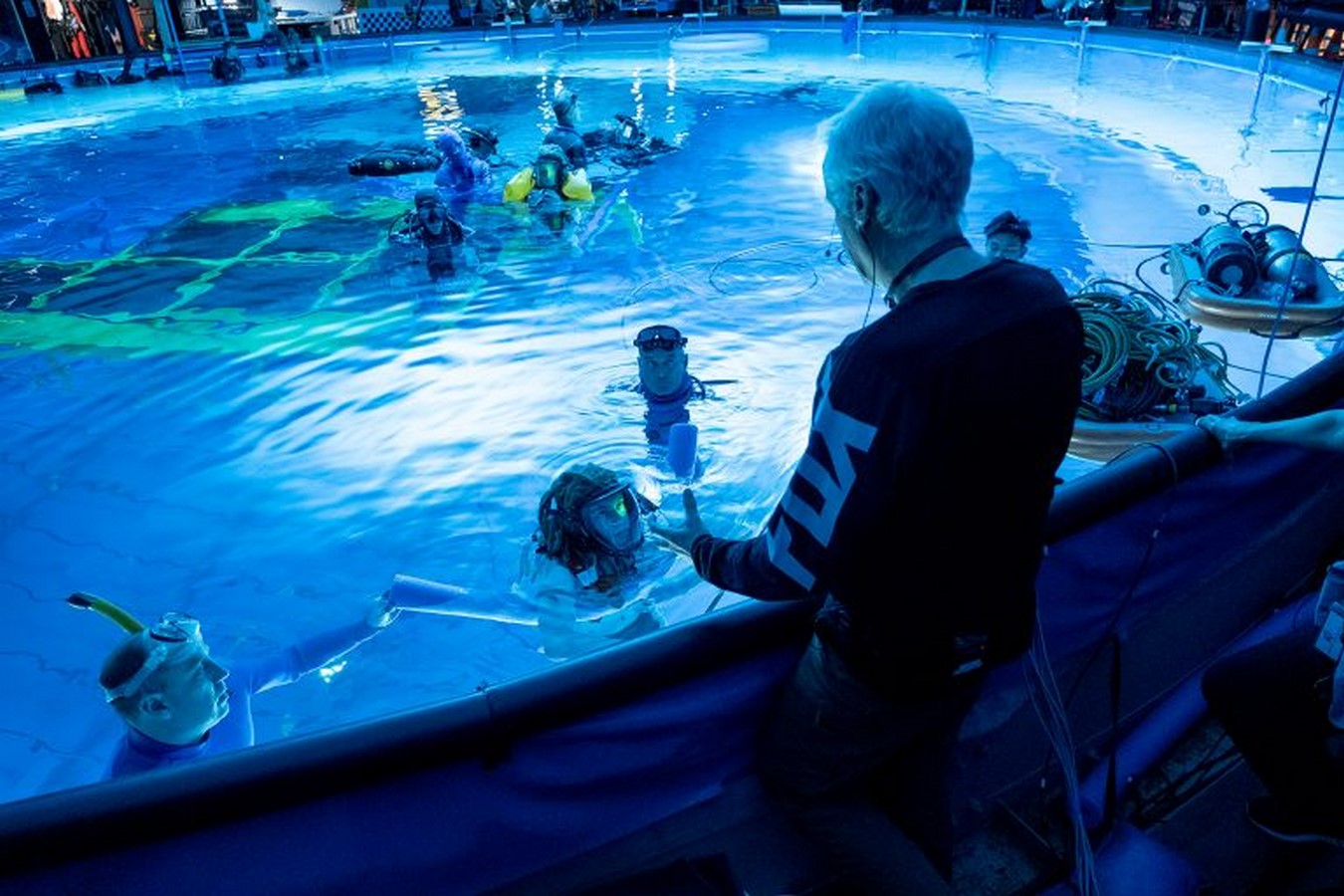

Recent trends in animated filmmaking lean toward 3D animation, driven by ongoing technological progress that makes it an increasingly favored medium in the industry.
The rise in AI art and a new market
The medium of art has moved from physical medium to virtual ones, in the same way artists have also been replaced by technology Artificial intelligence has taken the world by storm producing impressive artwork, but it lacks the subjective and emotional depth that informs human creativity and inherent morality. The creative process often demands a personal touch, with artists drawing inspiration from their distinct experiences, perspectives, and emotions to craft truly original works. Hence, AI has sparked division, with certain reservations surrounding the ethical considerations related to its use in the realm of art. Hence, even though AI-generated art represents an exciting addition to the art world, its growing reliance on artificial intelligence is posing a risk to the authenticity and creativity of artists. However, there is no denying that AI has capabilities that are beyond human capabilities to produce artwork in less than minutes, able to learn different styles and create art never seen before.

Technology has given rise to a movement akin to “pop art,” which places the audience at the forefront, rather than catering solely to intellectuals, and attempts to circumvent the entrenched art establishment. In the same way, a new way of monetizing art prioritizes an audience other than art intellectuals alone. This shift can be attributed to the introduction of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) that enable the acquisition of digital ownership for digital artworks. This represents a contemporary way of monetizing art within the digital landscape. This medium has enabled numerous artists who previously lacked viable avenues to sell and trade their creations to trade their work by generating income by embracing this digital currency phenomenon.NFTs offer a legitimate and beneficial means of compensating digital artists for their craft. Consequently, NFTs have become a pivotal facet of the 21st-century digital art creation and sales landscape.
A Shift in the Paradigm of Art
Hence, there is a major paradigm shift with the introduction of digital Technology where physical mediums of canvases, paper, etc. are replaced by virtual platforms, creators are replaced by AI, and art collectors are replaced by the common people. to create immersive experiences can be a new and innovative way to take art to a new level. Often change brings with it numerous newfound issues that need to be resolved for example authenticity. At the same time The capabilities of AI and AR, VR enable artists to express themselves in manners previously inconceivable. It presents an opportunity to unlock fresh modes of storytelling and self-expression, ultimately immersing viewers in more profound experiences and intensifying the emotional impact on spectators. This transformation beckons to embrace these possibilities creating immersive experiences through art.
References:
How AR Powers NFT Projects. (n.d.). artlabs. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://artlabs.ai/blog/how-ar-powers-nft-projects
Impact of Digital Technology on Art – 1605 Collective. (2023, April 6). 1605 Collective. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://1605collective.com/blogs/blogposts/impact-of-digital-technology-on-art
James, D. (2023, January 2). ‘Avatar’ plunges beneath the surface with new technology. Los Angeles Times. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://www.latimes.com/entertainment-arts/awards/story/2023-01-02/how-avatar-sequel-takes-its-technology-underwater-for-an-immersive-experience
A Look at the Latest Technologies Used in Digital Art. (2023, June 26). 21 Draw. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://www.21-draw.com/digital-art-technologies/
Milano, M. (2022, March 30). How AR artists can bring art to a new level. Inglobe Technologies. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://www.inglobetechnologies.com/how-ar-artists-can-bring-art-to-a-new-level/
Obare, E. (2023, March 3). The Purpose of Digital Art in Contemporary Culture. Arts Help. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://www.artshelp.com/digital-art-in-contemporary-culture-nfts/
Oen, K. G. (n.d.). teamLab: Continuity – Exhibitions. Asian Art Museum. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://exhibitions.asianart.org/exhibitions/teamlab-continuity/
The Role of Technology in Art – EDUCATION TODAY. (2022, April 8). Education Today. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://educationtoday.org.in/2022/04/08/the-role-of-technology-in-art/
Section 6: Overall Impact of Technology on the Arts. (2013, January 4). Pew Research Center. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2013/01/04/section-6-overall-impact-of-technology-on-the-arts/
Wiener, A. (2022, February 10). The Rise of “Immersive” Art. The New Yorker. Retrieved September 24, 2023, from https://www.newyorker.com/news/letter-from-silicon-valley/the-rise-and-rise-of-immersive-ar
















