An arid climate is characterized by having low rainfall and the climate is extreme. Rainfall in dry zones is often seasonal, but it is also quite unpredictable and with significant yearly variations in total precipitation. Extreme temperature changes (−2 to 48°C), prolonged daylight hours, strong winds (35–40 km/h), and therefore major evaporation are all experienced in the area. A necessity for the survival of humans is having access to water to meet basic requirements. However, water is becoming more and more scarce due to global warming which has an influence on water distribution processes from a socio-hydrological standpoint. It is crucial to understand how these water-human systems change in response to water constraints using sustainable and active standards. It is a crucial factor in architectural design and it greatly impacts a building’s functionality and energy usage. The following factors are considered to have better water-efficient strategies in construction in arid or water-scarce regions.
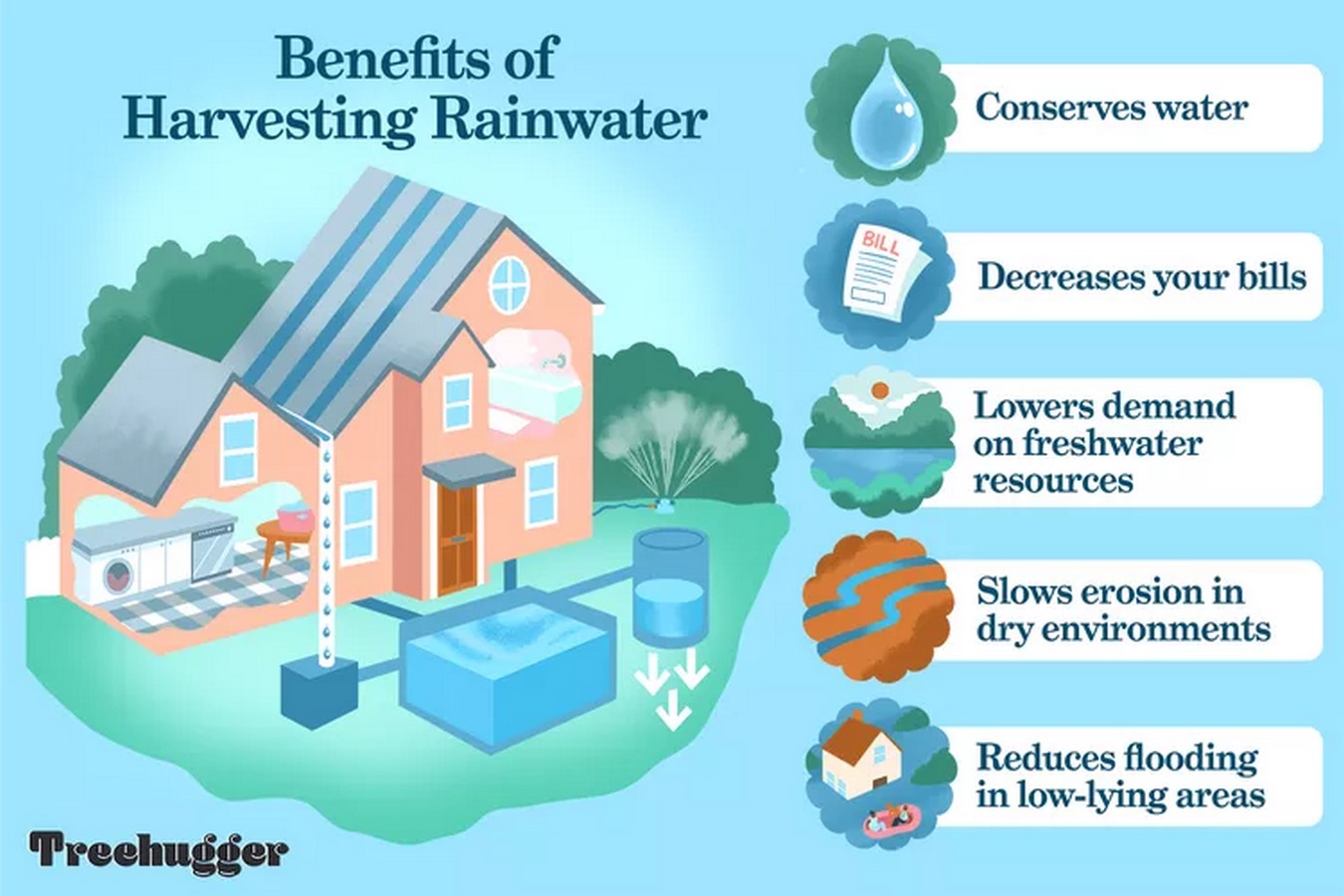
1. Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a technology that uses both basic methods like pots and tanks as well as complex methods to collect and store rainwater from roofs, land surfaces, or rock catchments for human use. To permit rainwater collecting, gutters and downpipes linked to tanks should be installed on all structures. Rainwater can be stored in above-ground PVC tanks, reinforced stabilized soil blocks or concrete tanks, or underground masonry or reinforced cement.
On-site, this water may be utilized again for irrigation, gardening, building, flushing, and cleaning. Rainwater collected from the roof can be used for cooking and drinking if it gets properly treated.
The following is a list of advantages of the rainwater collection system.
- Spend less.
- Lower the cost of the water bill.
- Lower the need for water.
- Lessen the requirement for water imports.
- Encourage energy and water conservation.
- Enhance both the amount and quality of groundwater.
- Filtration system for watering landscapes is not required.
- The installation and operation of this technology is very uncomplicated.
- It lessens the amount of fertilizers, pesticides, metals, and other pollutants that pollute surface water and cause floods, soil erosion, and stormwater runoff.
- It is great supply of water for landscape irrigation since it is devoid of minerals, dissolved salts, and contaminants.
However, precaution should be taken for water catchment. To keep leaves and other debris out of the system, mesh filters and sand filters should be placed at the mouths of drain pipes. Each tank need to have a drainage/recharge system linked to an overflow system.
2. Wastewater Recycling
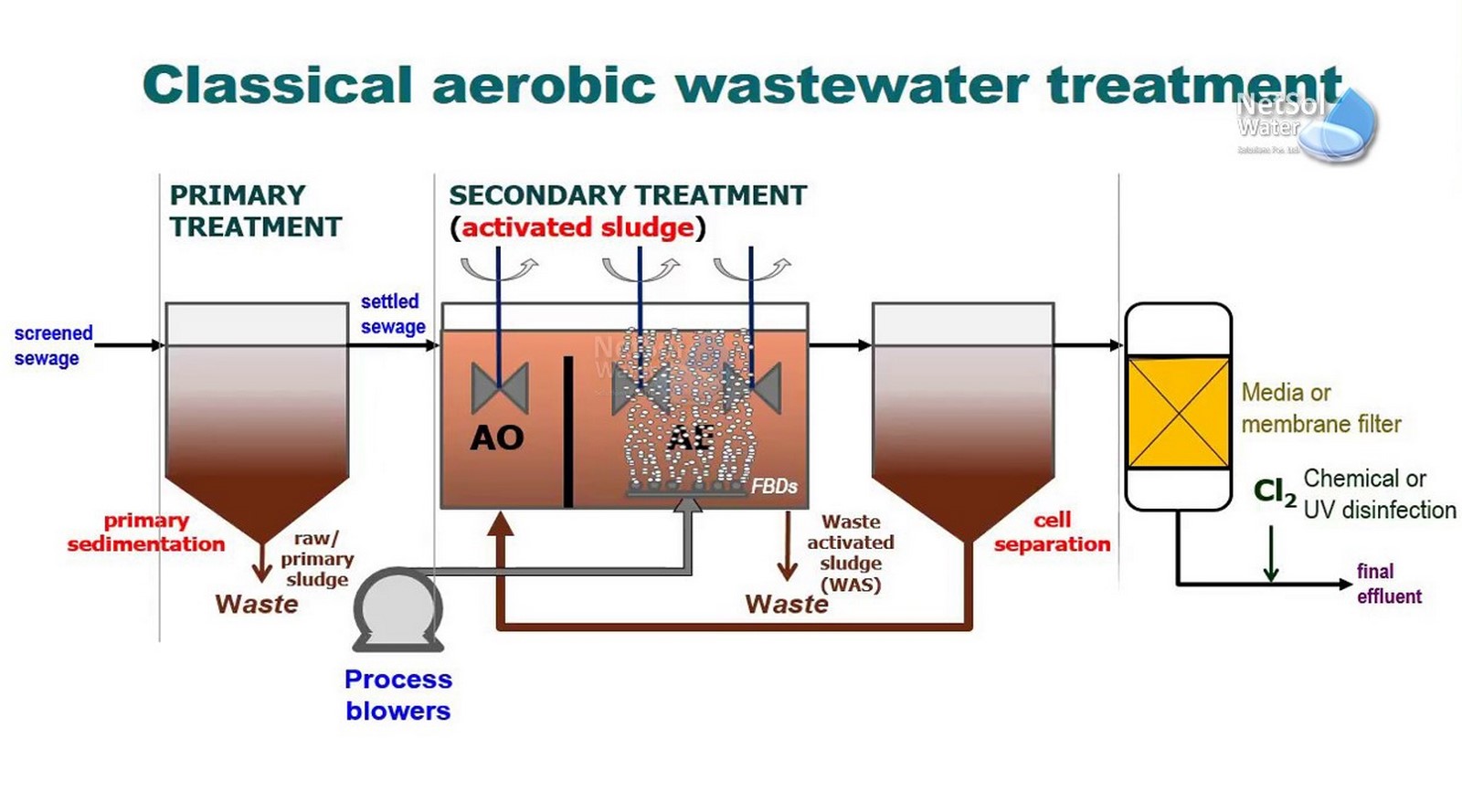
Groundwater treatment solutions are necessary for safe groundwater treatment. Various technologies are used in the wastewater recycling process, depending on the effluent’s intended use and its source. Greywater (from bathing, laundry, and cooking) and blackwater (from the toilet) are the two categories of wastewater. It’s called combined sewage when it’s mixed with stormwater. Gray water may be effectively treated with activated charcoal filters that are connected to a pump. Although they can eliminate both organic and inorganic substances, installing them in a plumbing outlet can be expensive.
The aerobic biological treatment method, which involves introducing oxygen into water storage tanks, is another technique utilized in wastewater recycling. Beneficial bacteria may break down organic pollutants in wastewater through aerobic biological treatment. It is feasible to place storage tanks in structures.
3. Drainage and wastewater management
Making a drainage water management strategy is primarily necessary to:
(i) Prevent monetary and agricultural losses due to salinization, waterlogging, and deteriorating water quality.
(ii) Address quality degradation of shared water resources and
(iii) Conserve water for various users in the event of current or anticipated water scarcity.
Furthermore, adhering to drainage water laws and regulations can serve as a powerful motivator for better drainage water management.
The following strategies can be used to mitigate these effects:
- Including storm water drainage channels beside and around buildings.
- Rainwater collection to lessen surface runoff and prevent storm overflow methods for draining water.
- Pavements, walkways, and other pervious or permeable surfaces are used for light-weight traffic and parking lots to let precipitation seep into the earth and lessen surface runoff
- Designing novel landscape elements including retention ponds, swales, rain gardens built ponds, etc., to collect rainwater from roads, walkways, and rooftops and let it gradually seep into the earth, restocking the water table.
- Stormwater treatment before release into public drains to reduce pollution.

Careful site preparation and landscaping are also crucial in planning the drainage system. It is necessary to reduce the amount of water used for grass lawns and high-maintenance decorative plants in arid areas. Rather, the emphasis should be on xeriscaping, which utilizes natural and drought-tolerant species. Xeriscaping reduces the use of irrigation and is visually appealing. It also supports the local ecosystem.
The issue of sustainability are critical in dry nations and areas, and a solution is desperately needed. This calls for enormous efforts, such as the further use of irrigation’s capacity to save water in agriculture, the creation of new resources like seawater desalination, the replacement of agriculture with other forms of economic activity, or the relocation of people.
References:
1.www.linkedin.com. (n.d.). What are the best practices for water conservation and management in arid regions? [online] Available at: https://www.linkedin.com/advice/3/what-best-practices-water-conservation-management [Accessed 29 Oct. 2023].
2.SUSTAINABLE BUILDING FOR HOT AND ARID AREAS MARSABIT COUNTY. (n.d.). Available at: https://www.hamk.fi/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Manual-on-Sustainable-Building-for-Hot-and-Arid-Areas.pdf.
3.AOS Treatment Solutions. (2018). Wastewater Recycling Systems In Buildings | Methods and Technology. [online] Available at: https://aosts.com/how-recycle-wastewater-in-building-systems-methods-technology/#:~:text=The%20wastewater%20recycling%20process%20involves [Accessed 29 Oct. 2023].














