Traversing boundaries from the virtual to the physical realm, the rapid technological advancement in architecture and design has never ceased to amaze us. What started as basic hand drafting and modelling has quickly overlapped with computer-based 2D and 3D drawings using multiple software and is now gradually moving onto the domain of 3D printing in architecture. While architects have already been using 3D printing to create conceptual models to visualise their designs, this method is also being explored to create final structures on-site. Smaller versions of 3D printers can be seen in the home of architects, designers, architecture schools, and industries. Taking this technology to the next level, we can see 3D printers being utilised to fabricate actual structures on-site with 3D-printed components in the future.

What is 3D Printing in Architecture?
3D printing in Architecture is closely linked to how traditional printers work. While normally printers use inkjet technology to draw on a 2D surface like paper, 3D printing utilises the same method. However, the ink is replaced by any other material, such as plastic, metal, resin, or steel, to create 3D models through layering the material. A 3D architectural printer requires a digital data file such as CAD, VRML, or STL to create precise 3D models with zero wastage.
The evolution of 3D printing can be traced back to the year 1988 when the American Engineer Charles Hull invented the process of 3D printing by using a digital data file to create a realistic physical model. Even Hull was surprised by his discovery and, simultaneously amazed by how this technology could change the face of the manufacturing industry in the future.
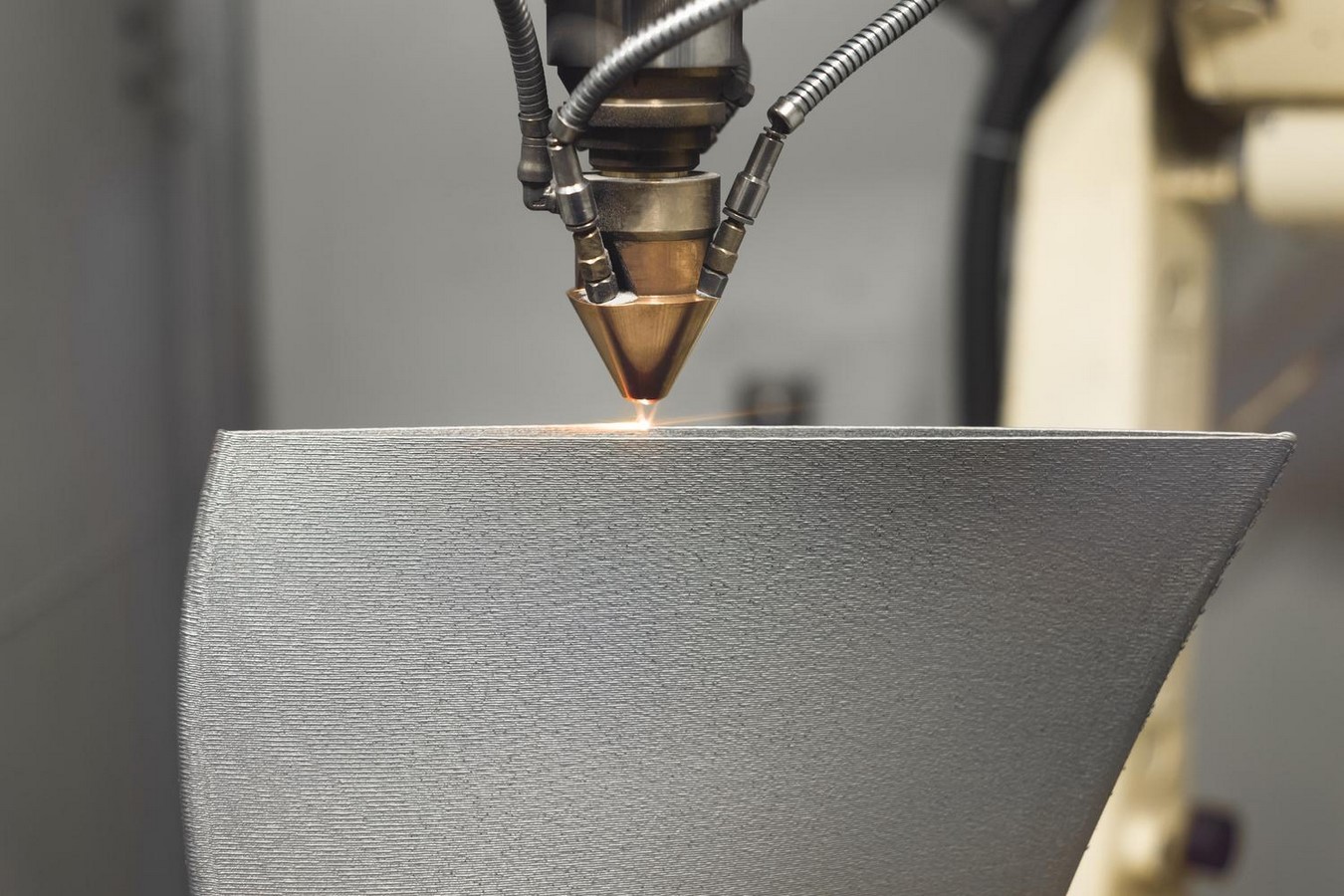
Opportunities and Advantages of 3D Printing
Negligible Wastage of Resources
Undeniably, the utilisation of 3D printing in architecture is highly advantageous for this industry which is crippled by the wastage of materials to build complex 3D models in a world that wants to be more sustainable in its use. The biggest advantage of this technology would be zero wastage of material due to the structure being built on-site and to a precise scale. This will ultimately lead to zero scrap waste generated while constructing a building manually.

Time-saving
No matter the amount of time on hand, an architect will always be short on deadlines and resources, but with 3D printing, this could change for the good. Through this efficient technology, architects can save both time and money by letting technology handle all the labour-intensive work, thus focusing more on project handling and designing. By producing a 3-month-long manual project in a matter of hours with better quality and precise precision using the material and colours of our choosing, 3D printing can greatly cut the workload of architects. For example, 3D printing can be utilised to create emergency housing shelters in just a few hours, as displayed by the Californian-based Mighty Buildings, which managed to print a housing unit in just 24 hours.
A Sustainable Process
3D printing can be used to explore new and sustainable materials in construction due to its efficient and faster approach to production. This will provide a more sustainable way to build by experimenting with greener and natural materials that reduce carbon emissions. For instance, by testing cutting-edge cement materials in 3D printing, Mighty Buildings and Fortera, a materials technology company, hope to reduce the carbon footprint of construction by reducing CO2 emissions by more than 60% compared to traditional cement.

The Challenges Faced by Experts
A Costly Affair
As 3D printing in Architecture is still a new technology in the market, buying the necessary machinery and equipment required for its use entails investing a large chunk of money in an architect or designer. The additional cost of materials, experimentation, and maintenance poses one of the greatest barriers for anyone willing to try this technology.
Lack of Known Materials at Present
Materials that can be printed and constructed in real time are essential for getting the best outcomes from 3D printing. The range of materials a 3D printer can use depends on the type of machinery. While less sophisticated 3D printers may only work with materials like plastic and polymers, more sophisticated printers can also work with metal, ceramic, and glass. Yet, the selection of materials that supports additive manufacturing is limited, restricting the widespread use of this technology. Furthermore, the characteristics of the material, which is 3D printed, differ vastly from the traditional materials. For example, a metal alloy injected through a nozzle versus a die-cast may exhibit different properties.

What Does 3D Printing Entail for the Future?
It is important to note that 3D printing does not allow us to print entire structures simultaneously, such as houses or buildings. That is nearly impossible. However, what will happen is that the whole unit will be fabricated in parts at a manufacturing unit and then combined to create the final design at the construction site. This also signifies that the potential of 3D printers will largely be defined by how architects utilize their knowledge and skills to break up and unite individual elements to create a whole.
We can find solutions to the issues of limited printable materials and expensive printing processes. In that case, the widespread usage of 3D printing in architecture in the future is plausible. Considering the large scale of architectural projects, project management and a skilled labor force would be key in driving any project. But using this cutting-edge technology would be very helpful in producing intricate geometric shapes while reducing waste and transportation expenses. One cannot possibly foresee the future but rather be hopeful and even amazed by the advancement that 3D printing will bring into the vast architectural field in the coming decades.

References:
Thajudeen, A. (2022) 3D printing in construction: Prospects and challenges, Structures Insider. Available at: https://www.structuresinsider.com/post/3d-printing-in-construction-prospects-and-challenges (Accessed: 17 May 2023).
Building the future with 3D printing and real-time visualization (2021) ArchDaily. Available at: https://www.archdaily.com/968146/building-the-future-with-3d-printing-and-real-time-visualization (Accessed: 18 May 2023).
The future of 3D printing for Architecture (2018) 3D Insider. Available at: https://3dinsider.com/3d-printing-architecture/ (Accessed: 20 May 2023).
What the future holds for 3D printing in architecture and Design (no date) Houzz. Available at: https://www.houzz.com/magazine/what-the-future-holds-for-3d-printing-in-architecture-and-design-stsetivw-vs~57915631 (Accessed: 21 May 2023).
(No date a) Meet the future of 3D-printed buildings | architect magazine. Available at: https://www.architectmagazine.com/technology/meet-the-future-of-3d-printed-buildings_o (Accessed: 21 May 2023).
Castenson, J. (2022) 3D printing offers outstanding sustainability benefits, while also avoiding supply chain issues, Forbes. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/jennifercastenson/2021/10/12/3d-printing-offers-outstanding-sustainability-benefits-while-also-avoiding-supply-chain-issues/?sh=550f61175eaf (Accessed: 21 May 2023).
Galloway, L. (2022) What are the biggest challenges for the 3D printing industry?, BMF Boston Micro Fabrication. Available at: https://bmf3d.com/blog/3d-printing-industry-challenges/#:~:text=Material%20selection%20is%20also%20challenging,enough%20to%20support%20additive%20manufacturing. (Accessed: 21 May 2023).

















